How To Choose Timer ICs: The Ultimate Guide
Timer Integrated Circuits (ICs) are essential components in a wide range of electronic devices, from simple blinking LED circuits to complex industrial automation systems. They are used to generate precise time delays, oscillations, and pulse signals. With a variety of timer ICs available in the market, choosing the right one for your application can be challenging. This guide will walk you through the key factors to consider when selecting a timer IC, ensuring you make an informed decision.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Timer ICs
Types of Timer ICs
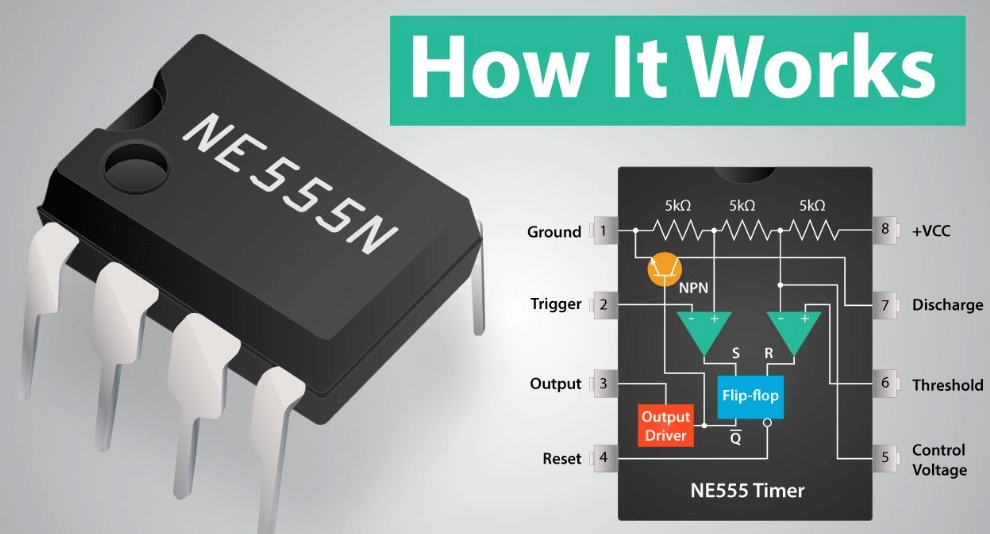
555 Timer IC
556 Dual Timer IC
558 Quad Timer IC
Programmable Timer ICs
Real-Time Clock (RTC) ICs
Key Parameters to Consider
Timing Range
Accuracy and Stability
Power Consumption
Supply Voltage Range
Output Current Capability
Package Type
Operating Temperature Range
Applications of Timer ICs
Pulse Generation
Oscillators
Time Delay Circuits
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
Sequential Timing
How to Choose the Right Timer IC
Define Your Application Requirements
Compare Specifications
Consider Cost and Availability
Evaluate Ease of Use
Check for Additional Features
Popular Timer ICs in the Market
NE555
LM556
DS3231 (RTC)
TLC555 (Low-Power Timer)
Conclusion
1. Introduction to Timer ICs
Timer ICs are specialized integrated circuits designed to produce accurate time delays or oscillations. They are widely used in various electronic applications, including consumer electronics, automotive systems, industrial control, and more. The most famous timer IC is the 555 timer, which has been a staple in electronics since its introduction in the 1970s.
2. Types of Timer ICs
555 Timer IC
The 555 timer IC is one of the most popular and versatile timer ICs available. It can operate in three modes:
Monostable Mode: Produces a single pulse of a specific duration.
Astable Mode: Generates a continuous square wave.
Bistable Mode: Acts as a flip-flop, with two stable states.
556 Dual Timer IC
The 556 timer IC is essentially two 555 timers in a single package. It is useful for applications requiring multiple timing functions.
558 Quad Timer IC
The 558 timer IC contains four 555 timers in one package, making it ideal for complex timing applications.
Programmable Timer ICs
Programmable timer ICs allow users to set timing parameters via software or external components. They offer greater flexibility and precision compared to fixed-function timers.
Real-Time Clock (RTC) ICs
RTC ICs are used in applications that require accurate timekeeping over long periods. They often include features like calendar functions and battery backup.
3. Key Parameters to Consider
Timing Range
The timing range refers to the minimum and maximum time intervals the timer IC can generate. Ensure the IC you choose can meet the timing requirements of your application.
Accuracy and Stability
Accuracy refers to how closely the timer IC can maintain the desired timing interval. Stability is the ability to maintain accuracy over time and under varying conditions. High-precision applications may require timer ICs with low drift and high stability.
Power Consumption
Power consumption is critical, especially in battery-powered devices. Low-power timer ICs can extend battery life and reduce heat generation.
Supply Voltage Range
The supply voltage range indicates the minimum and maximum voltages the timer IC can operate with. Ensure the IC is compatible with your system's power supply.
Output Current Capability
The output current capability determines how much current the timer IC can source or sink. This is important if the timer is driving external components like LEDs, relays, or motors.
Package Type
Timer ICs come in various package types, including DIP (Dual In-line Package), SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit), and SMD (Surface Mount Device). Choose a package that fits your PCB design and assembly process.
Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range specifies the minimum and maximum temperatures at which the timer IC can function reliably. Consider the environmental conditions of your application.
4. Applications of Timer ICs
Pulse Generation
Timer ICs are commonly used to generate precise pulses for triggering other circuits or devices.
Oscillators
In astable mode, timer ICs can function as oscillators, generating square waves for clock signals or tone generation.
Time Delay Circuits
Timer ICs can create precise time delays, useful in applications like power sequencing or debouncing switches.
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
Timer ICs can generate PWM signals for controlling motor speed, LED brightness, or other analog outputs.
Sequential Timing
Complex timing sequences can be achieved using multiple timer ICs or programmable timers.
5. How to Choose the Right Timer IC
Define Your Application Requirements
Start by clearly defining the requirements of your application, including timing range, accuracy, power consumption, and output current.
Compare Specifications
Compare the specifications of different timer ICs to find one that meets your requirements. Pay attention to timing range, accuracy, power consumption, and supply voltage.
Consider Cost and Availability
Cost and availability are practical considerations. Choose a timer IC that fits your budget and is readily available from reputable suppliers.
Evaluate Ease of Use
Consider the ease of use, including the availability of reference designs, application notes, and community support. Some timer ICs may require additional components or complex configurations.
Check for Additional Features
Some timer ICs offer additional features like programmable timing, low-power modes, or integrated oscillators. These features can simplify your design and add functionality.
6. Popular Timer ICs in the Market
NE555
The NE555 is the classic 555 timer IC, known for its versatility and ease of use. It is available in various packages and is widely used in hobbyist and professional projects.
LM556
The LM556 is a dual 555 timer IC, offering two independent timers in a single package. It is ideal for applications requiring multiple timing functions.
DS3231 (RTC)
The DS3231 is a highly accurate real-time clock IC with temperature compensation. It is commonly used in applications requiring precise timekeeping.
TLC555 (Low-Power Timer)
The TLC555 is a low-power version of the 555 timer IC, making it suitable for battery-powered applications.
Conclusion
Choosing the right timer IC for your application involves careful consideration of various factors, including timing range, accuracy, power consumption, and package type. By understanding your application requirements and comparing the specifications of different timer ICs, you can select the best component for your project. Whether you're designing a simple blinking LED circuit or a complex industrial control system, the right timer IC will ensure reliable and precise operation.
Remember to consider cost, availability, and ease of use, as well as any additional features that may enhance your design. With the right timer IC, you can achieve the precise timing and control needed for your electronic projects.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to choose timer ICs, covering everything from basic types to advanced considerations. By following this guide, you'll be well-equipped to select the perfect timer IC for your next project.
Kevin Chen
Founder / Writer at Rantle East Electronic Trading Co.,Limited
I am Kevin Chen, I graduated from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China in 2000. I am an electrical and electronic engineer with 23 years of experience, in charge of writting content for ICRFQ. I am willing use my experiences to create reliable and necessary electronic information to help our readers. We welcome readers to engage with us on various topics related to electronics such as IC chips, Diode, Transistor, Module, Relay, opticalcoupler, Connectors etc. Please feel free to share your thoughts and questions on these subjects with us. We look forward to hearing from you!







 Start With
Start With Include With
Include With


