The Essential World of Capacitors in Electric Appliances
In the vast landscape of electronic components, capacitors stand as silent workhorses powering our modern world. These seemingly simple devices play crucial roles in virtually every electronic appliance we use daily, from refrigerators to smartphones. Their ability to store and release electrical energy makes them indispensable in modern electronics.
Basic Principles
A capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. The fundamental relationship governing capacitors is given by the equation:
Where:
is capacitance in Farads
is the dielectric constant
is the plate area
is the distance between plates
Let's visualize a basic capacitor structure:
Basic Capacitor StructureClick to open artifact
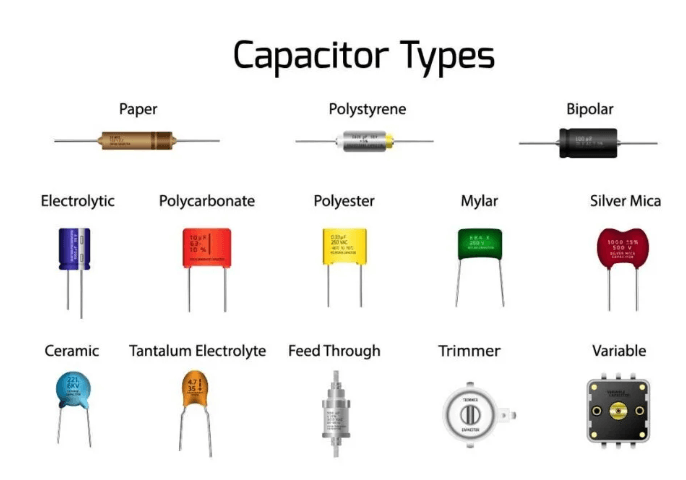
Types of Capacitors
Comparison Table of Common Capacitor Types
| Type | Capacitance Range | Voltage Range | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrolytic | 0.1 μF to 100,000 μF | 6.3V - 450V | Power supplies, Audio equipment | High capacitance, Low cost |
| Ceramic | 1 pF to 1 μF | 50V - 3000V | High-frequency circuits, Decoupling | Small size, Low inductance |
| Film | 100 pF to 100 μF | 50V - 2000V | Audio circuits, Motor run | Good stability, Self-healing |
| Supercapacitors | 1 F to 3000 F | 2.3V - 5.5V | Energy storage, Backup power | Extremely high capacitance |
Role in Home Appliances
1. Motor Applications
Start Capacitors: Provide initial high torque in single-phase motors
Run Capacitors: Maintain motor efficiency during operation
2. Power Supply Applications
Voltage smoothing after rectification
Ripple current reduction
Energy storage for temporary power loss
Let's visualize a basic power supply filtering circuit:
Power Supply FilteringClick to open artifact
Industrial and Specialized Applications
Variable Frequency Drives
DC link stabilization
Power factor correction
Medical Equipment
Defibrillator energy storage
X-ray machine power supplies
Consumer Electronics
Touchscreen coupling
Audio signal coupling
Flash photography
Recent Advances and Future Trends
Solid-state capacitors for improved reliability
Graphene-based supercapacitors
Integration with renewable energy systems
Miniaturization for mobile devices
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Common Failure Signs
Bulging or leaking electrolytic capacitors
Intermittent device operation
Humming or buzzing sounds in appliances
Device not starting properly
Safety Precautions
Always discharge capacitors before handling
Use proper tools for testing
Consider voltage ratings when replacing
Maintain proper polarity for electrolytic capacitors
Environmental Considerations
Proper disposal required for electronic waste
Recycling challenges due to mixed materials
RoHS compliance in modern capacitors
Energy efficiency improvements in newer designs
Conclusion
Capacitors remain fundamental to modern electronics, enabling efficient operation of countless devices. Understanding their principles and applications helps in better maintenance and troubleshooting of electronic appliances. As technology advances, capacitors continue to evolve, becoming more efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly.
Kevin Chen
Founder / Writer at Rantle East Electronic Trading Co.,Limited
I am Kevin Chen, I graduated from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China in 2000. I am an electrical and electronic engineer with 23 years of experience, in charge of writting content for ICRFQ. I am willing use my experiences to create reliable and necessary electronic information to help our readers. We welcome readers to engage with us on various topics related to electronics such as IC chips, Diode, Transistor, Module, Relay, opticalcoupler, Connectors etc. Please feel free to share your thoughts and questions on these subjects with us. We look forward to hearing from you!







 Start With
Start With Include With
Include With


