What Does a GND Symbol Mean in Electronics? Best Answer In 2025
What Does a GND Symbol Mean in Electronics?
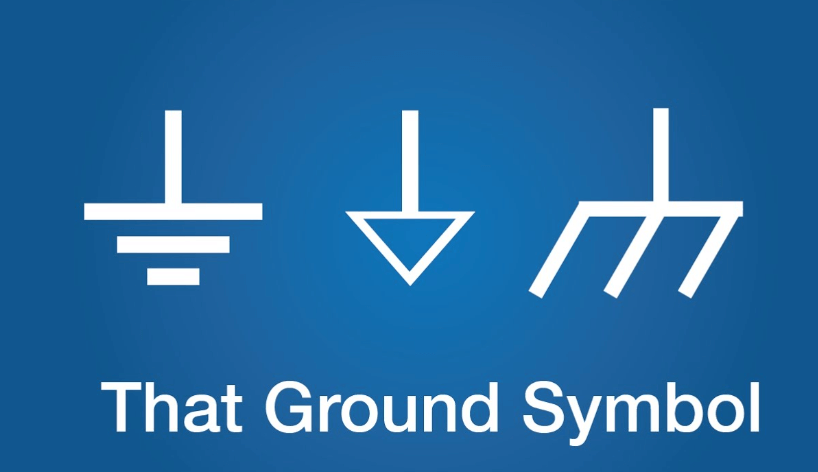
In the world of electronics, symbols are used to represent various components, connections, and concepts. One of the most common symbols you'll encounter is the GND symbol, which stands for Ground. Understanding what GND means and its role in electronic circuits is fundamental for anyone working with electronics, whether you're a hobbyist, student, or professional engineer.
What is Ground (GND)?
In electronics, Ground (GND) refers to a reference point in a circuit from which voltages are measured. It serves as a common return path for electric current and is often considered the zero-voltage reference point. While the term "ground" might suggest a connection to the earth, in most electronic circuits, it simply refers to a shared reference point rather than an actual connection to the physical ground.
The GND Symbol
The GND symbol is used in circuit diagrams to indicate the ground connection. There are several variations of the GND symbol, depending on the context and the type of ground being represented. Here are the most common ones:
Earth Ground:
This symbol represents a connection to the physical earth. It is often used in power systems and safety grounding.Chassis Ground:
This symbol indicates a connection to the metal chassis or enclosure of a device. It is used for shielding and safety purposes.Signal Ground:
This is the most common symbol in circuit diagrams. It represents the reference point for voltage measurements in a circuit.Virtual Ground:
This is not represented by a specific symbol but refers to a point in a circuit that is held at a reference voltage (not necessarily zero) for operational purposes, often seen in op-amp circuits.
Why is Ground Important?
Reference Point:
Ground provides a common reference point for measuring voltages in a circuit. All voltage measurements are taken relative to this point.Current Return Path:
In a closed circuit, current flows from the power source through the components and returns to the source via the ground connection.Safety:
In AC power systems, grounding ensures that excess current is safely directed to the earth, preventing electric shocks and damage to equipment.Noise Reduction:
Proper grounding helps reduce electrical noise and interference, which is critical in sensitive analog and digital circuits.
Practical Applications of Ground
Battery-Powered Circuits:
In battery-operated devices, the negative terminal of the battery is often designated as the ground.Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs):
PCBs typically have a ground plane, a large area of copper that acts as a common ground for all components.AC Mains Wiring:
In household wiring, the ground wire provides a safe path for fault currents, protecting users from electric shocks.Signal Integrity:
In high-frequency circuits, proper grounding ensures signal integrity by minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Floating Grounds:
A floating ground occurs when the ground reference is not properly connected, leading to unstable circuit behavior.Ground Loops:
Ground loops happen when there are multiple ground paths, causing unwanted currents and noise in the circuit.Ignoring Ground in PCB Design:
Poor grounding in PCB layouts can lead to noise, crosstalk, and malfunctioning circuits.
Conclusion
The GND symbol is a cornerstone of electronic circuit design, representing the reference point for voltage measurements and the return path for current. Whether you're designing a simple battery-powered device or a complex PCB, understanding and implementing proper grounding techniques is essential for ensuring the functionality, safety, and reliability of your circuit.
Next time you see a GND symbol in a schematic, you'll know it's more than just a simple connection—it's the foundation upon which the entire circuit operates!
Kevin Chen
Founder / Writer at Rantle East Electronic Trading Co.,Limited
I am Kevin Chen, I graduated from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China in 2000. I am an electrical and electronic engineer with 23 years of experience, in charge of writting content for ICRFQ. I am willing use my experiences to create reliable and necessary electronic information to help our readers. We welcome readers to engage with us on various topics related to electronics such as IC chips, Diode, Transistor, Module, Relay, opticalcoupler, Connectors etc. Please feel free to share your thoughts and questions on these subjects with us. We look forward to hearing from you!







 Start With
Start With Include With
Include With





