What is 2N3904 Silicon NPN Transistor: A Comprehensive Guide
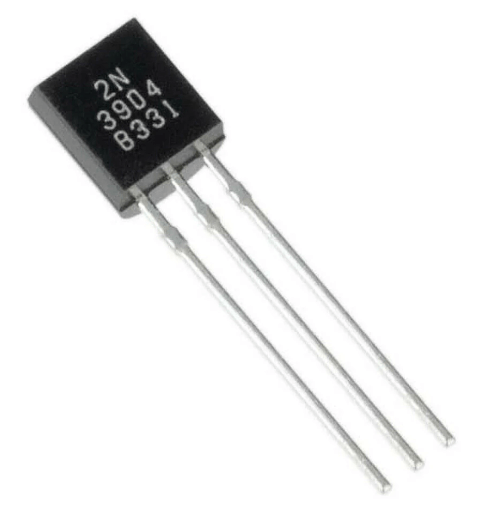
The 2N3904 is a widely used bipolar junction transistor (BJT) of the NPN type, fabricated from silicon. Introduced in the 1960s, it remains a staple in electronics due to its reliability, low cost, and versatility. Designed for low-power amplification and switching, it operates effectively in a variety of circuits, from hobbyist projects to industrial applications.
Key Features and Specifications
Maximum Ratings:
Collector-Emitter Voltage (V_CEO): 40 V
Collector-Base Voltage (V_CBO): 60 V
Emitter-Base Voltage (V_EBO): 6 V
Continuous Collector Current (I_C): 200 mA
Total Power Dissipation (P_tot): 625 mW (at 25°C)
Operating Temperature Range: -55°C to +150°C
Electrical Characteristics:
DC Current Gain (h_FE): 100–300 (varies with collector current and temperature)
Transition Frequency (f_T): 300 MHz (typical)
Saturation Voltages:
V_CE(sat): 0.2 V (at Ic=10 mA, Ib=1 mA)
V_BE(sat): 0.65–0.85 V (active region)
Package and Pin Configuration
The 2N3904 is housed in a TO-92 plastic package, with pins arranged as follows (front view, flat side facing you):
Emitter (E): Left pin.
Base (B): Middle pin.
Collector (C): Right pin.
Applications
Amplification: Used in small-signal amplification (e.g., audio preamps, RF stages) due to moderate gain and bandwidth.
Switching: Capable of switching loads up to 200 mA (e.g., LEDs, relays).
Darlington Pairs: Combined with PNP transistors (e.g., 2N3906) for high-gain configurations.
Oscillators and Signal Generators: Utilized in LC or RC oscillator circuits.
Voltage Regulators: Acts as a pass element in low-power regulator designs.
Comparisons with Similar Transistors
2N2222: Higher current capacity (800 mA) but lower f_T (250 MHz); packaged in TO-18.
BC547: Comparable specs, but pin configuration may differ.
2N4401: Higher I_C (600 mA) and power dissipation.
Thermal Considerations
Power Dissipation: Exceeding 625 mW without a heat sink risks thermal damage.
Thermal Runaway: Mitigated by using emitter resistors and proper biasing.
Example Circuits
Switching Circuit:
Conditions: Vcc=5V, LED Vf=2V, Ic=10 mA.
Rc = (5V - 2V - 0.2V)/10 mA = 280 Ω.
Assuming hFE=100, Ib=0.1 mA.
Rb = (5V - 0.7V)/0.1 mA ≈ 43 kΩ (use 10 kΩ for saturation).
Driving an LED:
Common-Emitter Amplifier:
Midpoint biasing for linear operation.
Voltage Gain ≈ Rc/Re (with bypassed emitter resistor).
Testing and Troubleshooting
Multimeter Testing:
Base-Emitter/Base-Collector junctions behave like diodes (conduct in forward bias).
Emitter-Collector should be open in reverse bias.
Common Issues:
Overheating due to excessive current.
Incorrect pin configuration or missing base resistor.
Alternatives
BC547, 2N4401, PN2222 (TO-92 version of 2N2222).
Conclusion
The 2N3904’s enduring popularity stems from its adaptability in low-power applications, cost-effectiveness, and robust performance. Whether amplifying signals or switching loads, it remains a cornerstone of electronic design, supported by a wealth of documentation and complementary components like the 2N3906 PNP transistor. Engineers and hobbyists alike continue to rely on this transistor for its proven reliability and ease of use.
Kevin Chen
Founder / Writer at Rantle East Electronic Trading Co.,Limited
I am Kevin Chen, I graduated from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China in 2000. I am an electrical and electronic engineer with 23 years of experience, in charge of writting content for ICRFQ. I am willing use my experiences to create reliable and necessary electronic information to help our readers. We welcome readers to engage with us on various topics related to electronics such as IC chips, Diode, Transistor, Module, Relay, opticalcoupler, Connectors etc. Please feel free to share your thoughts and questions on these subjects with us. We look forward to hearing from you!







 Start With
Start With Include With
Include With


