Differences Between Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors
Resistors are fundamental components in electronics, used to control the flow of electric current. Among the various types of resistors, pull-up and pull-down resistors play a critical role in digital circuits, particularly in ensuring stable logic states on input pins of microcontrollers, FPGAs, and other digital devices. This article explores the differences between pull-up and pull-down resistors, their applications, and how they function in circuits.
1. What Are Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors?
Pull-Up Resistors
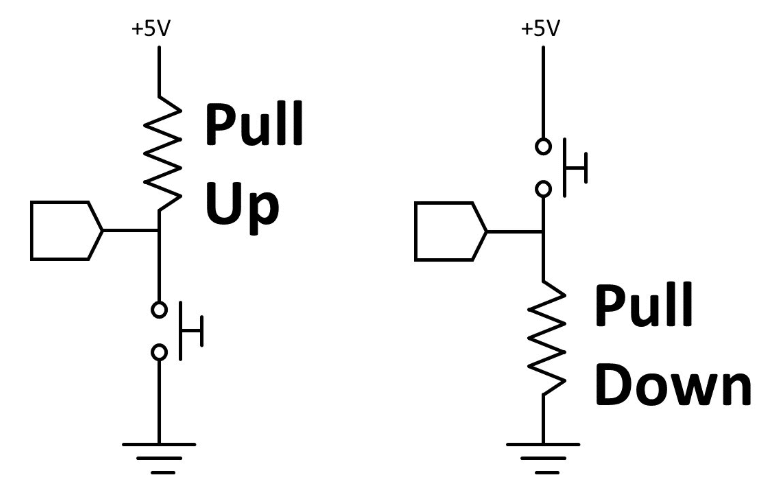
A pull-up resistor is a resistor connected between a signal line and the positive supply voltage (Vcc or Vdd). Its purpose is to ensure that the signal line is in a high logic state (1) when no other active device is driving it.
Pull-Down Resistors
A pull-down resistor is a resistor connected between a signal line and ground (GND). Its purpose is to ensure that the signal line is in a low logic state (0) when no other active device is driving it.
Both types of resistors are used to prevent floating inputs, which can cause unpredictable behavior in digital circuits.
2. How Do They Work?
Pull-Up Resistor Operation
When a switch or input is open, the pull-up resistor pulls the voltage on the input pin up to Vcc, ensuring a high logic state.
When the switch or input is closed, the input pin is connected directly to ground, overriding the pull-up resistor and resulting in a low logic state.
Pull-Down Resistor Operation
When a switch or input is open, the pull-down resistor pulls the voltage on the input pin down to ground, ensuring a low logic state.
When the switch or input is closed, the input pin is connected directly to Vcc, overriding the pull-down resistor and resulting in a high logic state.
3. Key Differences Between Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors
| Aspect | Pull-Up Resistor | Pull-Down Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| Connection | Connected between signal line and Vcc | Connected between signal line and GND |
| Default State | Ensures a high logic state (1) when idle | Ensures a low logic state (0) when idle |
| Active State | Low logic state (0) when activated | High logic state (1) when activated |
| Common Applications | Buttons, switches, I2C communication | Buttons, switches, digital logic circuits |
| Power Consumption | Consumes more power when active (low state) | Consumes more power when active (high state) |
| Noise Immunity | Better for noise immunity in high-state logic | Better for noise immunity in low-state logic |
4. Applications of Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors
Pull-Up Resistor Applications
Digital Inputs: Used to ensure a default high state on microcontroller input pins.
I2C Communication: Pull-up resistors are used on the SDA and SCL lines to ensure proper communication.
Open-Drain Outputs: Used to pull the output to a high state when the transistor is off.
Pull-Down Resistor Applications
Digital Inputs: Used to ensure a default low state on microcontroller input pins.
Push-Button Circuits: Ensures the input pin reads low when the button is not pressed.
Transistor-Based Circuits: Used to keep the base of a transistor at a low state when no signal is applied.
5. Choosing the Right Resistor Value
The value of the pull-up or pull-down resistor is critical for proper circuit operation. Typical values range from 1kΩ to 10kΩ, but the exact value depends on the following factors:
Factors to Consider:
Power Consumption: Lower resistor values draw more current, increasing power consumption.
Signal Rise Time: Higher resistor values increase the RC time constant, which can slow down signal transitions.
Noise Immunity: Lower resistor values provide better noise immunity but at the cost of higher power consumption.
Example Calculations:
For a 5V system with a desired current of 0.5mA:
6. Advantages and Disadvantages
Pull-Up Resistors
Advantages:
Ensures a known high state when no input is present.
Commonly used in communication protocols like I2C.
Disadvantages:
Higher power consumption when the input is active (low state).
Pull-Down Resistors
Advantages:
Ensures a known low state when no input is present.
Lower power consumption when the input is active (high state).
Disadvantages:
Less commonly used in certain communication protocols.
Conclusion
Pull-up and pull-down resistors are essential components in digital circuits, ensuring stable logic states and preventing floating inputs. While they serve similar purposes, their applications and behaviors differ based on their connection to Vcc or GND. Understanding their differences and proper usage is crucial for designing reliable and efficient electronic systems.
By selecting the appropriate resistor value and type, engineers can optimize power consumption, noise immunity, and signal integrity in their designs. Whether you're working with microcontrollers, communication protocols, or simple button circuits, pull-up and pull-down resistors are indispensable tools in your electronics toolkit.
Kevin Chen
Founder / Writer at Rantle East Electronic Trading Co.,Limited
I am Kevin Chen, I graduated from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China in 2000. I am an electrical and electronic engineer with 23 years of experience, in charge of writting content for ICRFQ. I am willing use my experiences to create reliable and necessary electronic information to help our readers. We welcome readers to engage with us on various topics related to electronics such as IC chips, Diode, Transistor, Module, Relay, opticalcoupler, Connectors etc. Please feel free to share your thoughts and questions on these subjects with us. We look forward to hearing from you!







 Start With
Start With Include With
Include With


