The C945 Transistor: A Comprehensive Guide
The C945 transistor (often designated as 2SC945 in full) is a widely used bipolar junction transistor (BJT) belonging to the NPN type. Originating from Japanese semiconductor manufacturers like Toshiba, this transistor is part of the JIS (Japanese Industrial Standard) naming convention, where "2S" denotes a bipolar transistor, "C" indicates NPN polarity, and "945" is the specific model number. Renowned for its reliability and versatility, the C945 is a staple in low-power amplification and switching applications across consumer electronics, hobbyist projects, and industrial systems.
Key Specifications
Below are the critical electrical and thermal characteristics of the C945 transistor, derived from datasheets:
Electrical Ratings
Collector-Emitter Voltage (V_CEO): 50 V
Collector-Base Voltage (V_CBO): 60 V
Emitter-Base Voltage (V_EBO): 5 V
Continuous Collector Current (I_C): 150 mA
Peak Collector Current (I_CM): 300 mA (pulsed)
Power Dissipation (P_D): 250 mW (at 25°C)
Gain and Frequency
DC Current Gain (hFE): 70–700 (varies by suffix code, e.g., GR: 200–400, O: 70–140, Y: 240–800)
Transition Frequency (f_T): 250 MHz (typical)
Thermal Characteristics
Operating Temperature Range: -55°C to +150°C
Storage Temperature Range: -55°C to +150°C
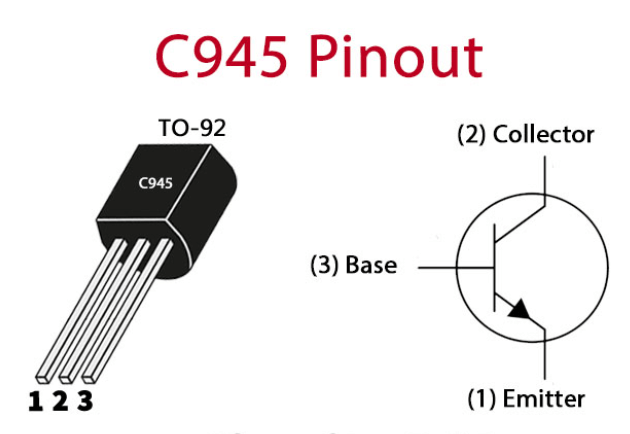
Physical Package and Pin Configuration
The C945 is housed in a TO-92 plastic package, compact and suitable for through-hole PCB mounting. The pin configuration (viewed from the flat side with leads downward) is typically:
Emitter (E)
Base (B)
Collector (C)
Note: Pin layouts can vary slightly between manufacturers. Always verify using the datasheet for your specific component.
Applications
The C945 excels in low-to-moderate frequency applications due to its balanced gain and speed. Common uses include:
1. Signal Amplification
Audio preamplifiers, RF stages, and sensor interfaces.
Example: A common-emitter amplifier for boosting microphone signals.
2. Switching Circuits
Driving LEDs, relays, or small motors (up to 150 mA).
Example: Microcontroller-driven LED activation via a base resistor.
3. Oscillators and RF Circuits
LC oscillators and radio frequency modules (f_T up to 250 MHz).
4. Consumer Electronics
Found in TVs, radios, and toys for signal processing and control.
Equivalent Transistors
If the C945 is unavailable, consider these substitutes after verifying voltage/current requirements:
2N3904: Lower V_CEO (40 V) but higher I_C (200 mA).
BC547: Similar specs (45 V, 100 mA), common in European designs.
2N2222: Higher I_C (800 mA) but lower V_CEO (40 V).
KSC945: Direct equivalent by Fairchild/ON Semiconductor.
Complementary PNP Pair: 2SA733 or 2N3906 for push-pull configurations.
Circuit Example: Common-Emitter Amplifier
A basic audio amplifier using the C945:
Biasing: Voltage divider network (R1, R2) sets the base voltage.
Input/Output Coupling: Capacitors (C1, C2) block DC.
Emitter Resistor (R_E): Stabilizes gain and temperature drift.
Adjust resistor values based on desired gain and operating point.
Usage Considerations
Voltage/Current Limits: Avoid exceeding V_CEO = 50 V or I_C = 150 mA.
Heat Dissipation: Use heatsinks if operating near P_D = 250 mW.
Static Protection: Handle with ESD-safe tools to prevent damage.
Biasing: Ensure proper base current to avoid saturation/cutoff.
Conclusion
The C945 transistor remains a versatile, cost-effective solution for amplification and switching tasks. Its robust specs, wide availability, and compatibility with substitutes make it a favorite among engineers and hobbyists. Whether you’re designing a radio receiver or a microcontroller-driven switch, the C945 offers a reliable performance foundation.
Kevin Chen
Founder / Writer at Rantle East Electronic Trading Co.,Limited
I am Kevin Chen, I graduated from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China in 2000. I am an electrical and electronic engineer with 23 years of experience, in charge of writting content for ICRFQ. I am willing use my experiences to create reliable and necessary electronic information to help our readers. We welcome readers to engage with us on various topics related to electronics such as IC chips, Diode, Transistor, Module, Relay, opticalcoupler, Connectors etc. Please feel free to share your thoughts and questions on these subjects with us. We look forward to hearing from you!







 Start With
Start With Include With
Include With


