What is a variable capacitor?
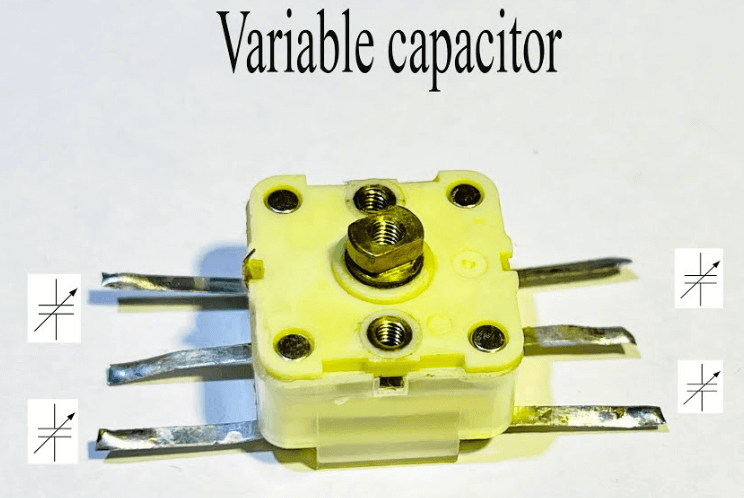
A variable capacitor is an electronic component designed to provide adjustable capacitance in circuits. Unlike fixed capacitors, its capacitance can be modified mechanically (via physical adjustment) or electronically (using voltage control). This adaptability makes it indispensable in tuning circuits, radio frequency (RF) systems, and applications requiring precise frequency control.
2. Working Principle
Variable capacitors operate on the fundamental equation of capacitance:
Where:
: Capacitance (in Farads)
: Permittivity of the dielectric material
: Overlapping area between plates
: Distance between plates
By rotating the movable plates (rotor) relative to the stationary plates (stator), the overlapping area changes, thereby altering capacitance. Mechanical types adjust , while electronic variants (e.g., varactors) modulate or via voltage.
3. Types of Variable Capacitors
3.1 Mechanical Variable Capacitors
Air-Gap Capacitors:
Use air as the dielectric.
Common in vintage radios for tuning.
Capacitance range: 10–500 pF.
Vacuum Variable Capacitors:
Enclosed in vacuum to handle high voltages (e.g., RF transmitters).
Trimmer Capacitors:
Small, screw-adjusted components for calibration.
Dielectric materials: Ceramic or plastic.
3.2 Electronic Variable Capacitors
Varactor Diodes:
Reverse-biased diodes where capacitance decreases with increasing voltage .
Used in voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs).
MEMS Capacitors:
Micro-electromechanical systems adjust via electrostatic actuation.
Ideal for compact, high-frequency devices.
4. Key Applications
Tuning Circuits: Select specific frequencies in radios/TVs.
Impedance Matching: Optimize power transfer in RF amplifiers.
Oscillators: Stabilize frequency in VCOs and phase-locked loops (PLLs).
Test Equipment: Calibrate resonant circuits in labs.
Wireless Communication: 5G systems and software-defined radios (SDRs).
5. Historical Evolution
1920s–1940s: Dominated by air-gap capacitors in analog radios.
1950s: Miniaturization led to trimmer capacitors.
1960s: Varactors enabled electronic tuning, replacing manual adjustments.
2000s–Present: MEMS and IC-integrated capacitors support IoT and mobile tech.
6. Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Typical Range/Value | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance Range | 1 pF – 1 nF | Determines tuning flexibility. |
| Voltage Rating | 50 V – 30 kV | Critical for high-power systems. |
| Q Factor | 100–10,000 | Indicates energy efficiency. |
| Temperature Stability | ±50 ppm/°C | Ensures reliability in varying environments. |
7. Advantages & Limitations
Pros:
Adjustable for dynamic circuit needs.
High Q factors (e.g., air-gap: Q > 1,000).
Reliable in harsh conditions (vacuum types).
Cons:
Mechanical wear in manual types.
Limited range compared to fixed capacitors.
Varactors require stable voltage sources.
8. Future Trends
Semiconductor Integration: Co-packaging varactors with ICs for compact designs.
MEMS Advancements: Sub-1 GHz to THz applications in 6G networks.
Smart Materials: Dielectrics with tunable permittivity (e.g., ferroelectrics).
Conclusion
Variable capacitors bridge the gap between static components and adaptive electronics. From vintage radios to cutting-edge 5G systems, their ability to fine-tune capacitance ensures enduring relevance in evolving technologies. As wireless communication and IoT expand, innovations in MEMS and material science will drive their next-generation applications.
Kevin Chen
Founder / Writer at Rantle East Electronic Trading Co.,Limited
I am Kevin Chen, I graduated from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China in 2000. I am an electrical and electronic engineer with 23 years of experience, in charge of writting content for ICRFQ. I am willing use my experiences to create reliable and necessary electronic information to help our readers. We welcome readers to engage with us on various topics related to electronics such as IC chips, Diode, Transistor, Module, Relay, opticalcoupler, Connectors etc. Please feel free to share your thoughts and questions on these subjects with us. We look forward to hearing from you!







 Start With
Start With Include With
Include With


